Mastering JavaScript’s call, apply, and bind – The Easy Way!

Have you ever been confused about call, apply, and bind in JavaScript? Don’t worry, you’re not alone! These three methods are powerful, but they can be tricky to understand at first. In this article, we’ll break them down in the simplest way possible with examples that make sense.
What Are call, apply, and bind?
All three of these functions are used to control this keyword in JavaScript. When working with objects and functions, sometimes you need to tell JavaScript what this should refer to explicitly. That’s where these methods come in!
Let’s take a look at each one.
1. call – Execute a Function Immediately
The call method is used to invoke a function immediately and explicitly set the value of this.
Syntax:
functionName.call(thisArg, arg1, arg2, …)
Example:
const person = {
name: “Alice”
};
function greet(age) {
console.log(`Hello, my name is ${this.name} and I am ${age} years old.`);
}
greet.call(person, 25); // Hello, my name is Alice and I am 25 years old.
Here, call sets this to person, so the function correctly accesses person.name.
2. apply – Similar to call, But Uses an Array
The apply method is almost the same as call, but instead of passing arguments one by one, you pass them as an array.
Syntax:
functionName.apply(thisArg, [arg1, arg2, …])
Example:
greet.apply(person, [25]); // Hello, my name is Alice and I am 25 years old.
This is useful when you already have an array of arguments and don’t want to manually pass each one.
3. bind – Returns a New Function
The bind method doesn’t execute the function immediately. Instead, it returns a new function with this permanently set to the specified value.
Syntax:
const newFunction = functionName.bind(thisArg, arg1, arg2, …)
Example:
const boundGreet = greet.bind(person, 25);
boundGreet(); // Hello, my name is Alice and I am 25 years old.
Now boundGreet is a function that will always use person as this, no matter how or when it’s called.
Differences at a Glance
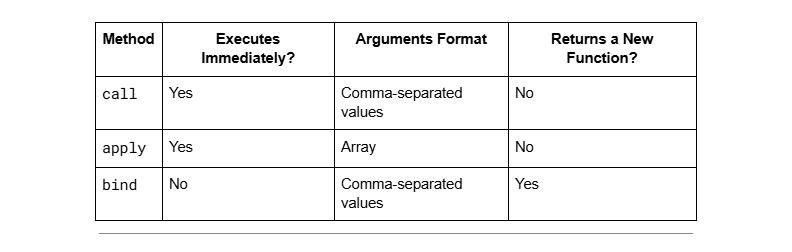
When Should You Use Each?
- Use call when you want to invoke a function immediately and pass arguments one by one.
- Use apply when you want to invoke a function immediately but have arguments in an array.
- Use bind to create a new function with a specific value.
Final Thoughts
Understanding call, apply, and bind will make you a better JavaScript developer. They are essential for handling this in a controlled way and can help you write cleaner, more flexible code.
At LN Webworks, we specialize in creating high-performance JavaScript solutions that offer seamless user experiences. Whether it’s custom web development, advanced UI/UX, or scalable applications, our expert team ensures that your projects are built with the best coding practices.
Ready to take your JavaScript skills—or your web development projects—to the next level? Contact LN Webworks today!
