PHP Attributes In Drupal Development: All You Need To Know

Drupal is moving ahead with PHP attributes. Introduced in PHP 8.1, this feature is changing how developers define plugins and manage their metadata. But there’s a lot more that comes with it.
First and foremost, PHP attributes are a native feature of PHP 8.1. It eliminates the need for external libraries like “doctrine/annotations.” This simplifies the development process by keeping code clean and concise.
Furthermore, modern IDEs offer better support for attributes. They provide features like code completion and validation, making your workflow significantly more efficient. And because attributes are a core part of the PHP language, you can rest assured that they’ll receive ongoing development and support in future PHP versions. All of this ensures that your code remains compatible and up-to-date as Drupal evolves.
However, one question that comes up very often is why PHP attributes in the first place. Well, let’s understand this by knowing the limitations of annotations.
Why PHP Attributes?
Previously, Drupal relied on annotations (powered by the “doctrine/annotations” library) to provide metadata and configuration for plugins. While annotations served their purpose, they introduced certain limitations:
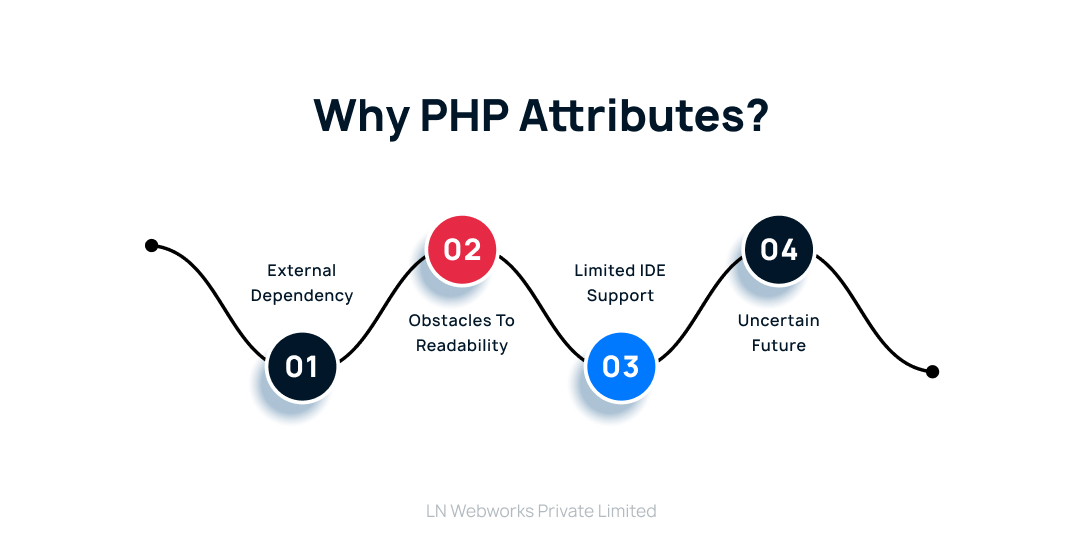
External Dependency
Annotations necessitated the use of an external library, “doctrine/annotations,” which added complexity to the development environment. Attributes, being a native feature, eliminate this dependency.
Obstacles to Readability
Annotations were based on doc blocks, which can be lengthy and aesthetically complex. Code clarity is increased via attribute syntax, which is more succinct and simpler to understand.
Limited IDE Support
In comparison to attributes, IDE support for annotations was less extensive. Advanced IDE capabilities like code completion and validation help attributes and make the development process more efficient.
Uncertain Future
Because annotations are an external library, it was unclear how Drupal would support and develop them in the future. As a fundamental component of PHP, attributes are here to stay and will probably continue to be improved along with the PHP language. This guarantees that any future versions of your Drupal code that use attributes will still work with it.
Attributes in Action: Defining Drupal Plugins
Drupal is currently moving its plugin definition from annotations to attributes. This is an explanation of how it functions:
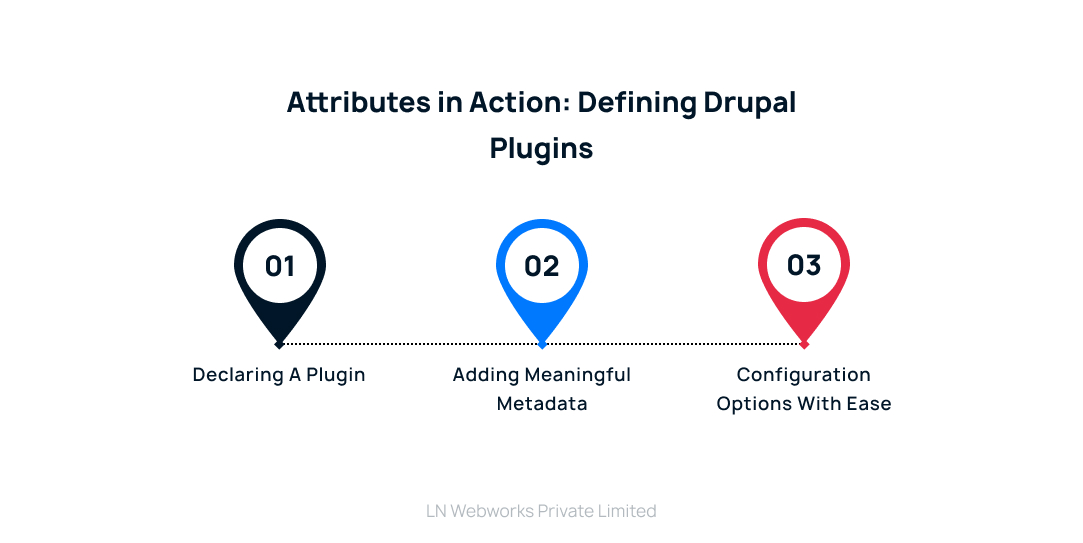
Declaring a Plugin
To designate a class as a plugin, use the #[PluginType] attribute. The sort of plugin you are creating, such as a block, action, or field, is specified by this attribute.
Adding Meaningful Metadata
Attributes like #[Label] and #[Description] provide essential metadata for your plugin. The #[Label] attribute defines a human-readable label that will be used to identify your plugin within the Drupal interface. The #[Description] attribute allows you to provide a clear and concise explanation of what your plugin does.
Configuration Options with Ease
You can leverage attributes like #[ConfigFactory] to associate a configuration form with your plugin. This configuration form enables users to customize the behavior of your plugin within the Drupal administration interface.
Core Benefits of PHP Attributes for Developers
For Drupal developers, the move to attributes has various benefits:
Simpler Code
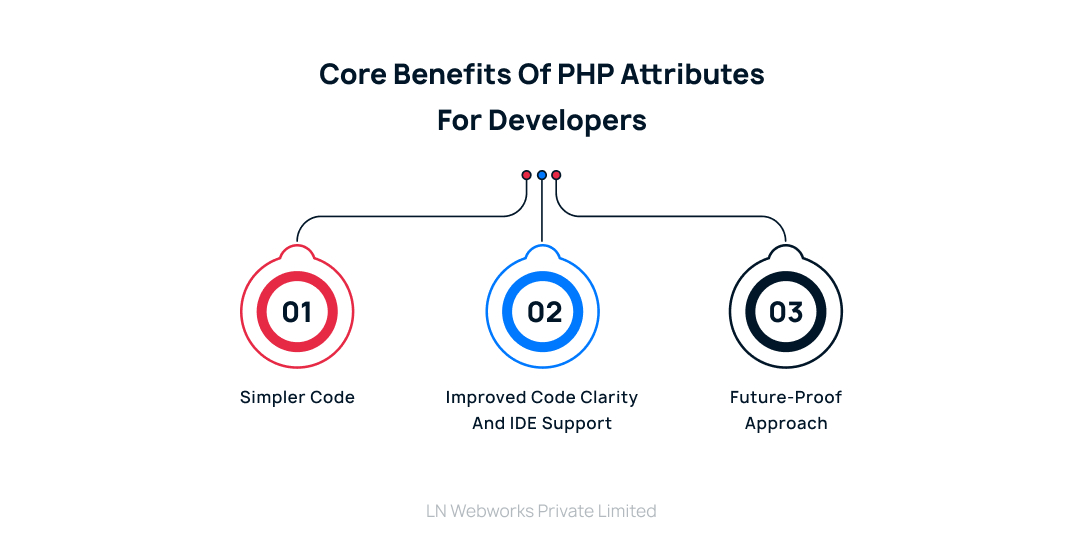
It is simpler to write, read, and maintain code with cleaner syntax and native integration.
Improved Code Clarity and IDE Support
These two factors contribute to an overall improved developer experience.
Future-Proof Approach
Developers can make sure their code is compatible with upcoming Drupal versions by utilizing the newest PHP technologies.
Getting Started with Attributes
Here are steps to get started with PHP attributes in Drupal, focusing on the recommended approach for new development:
1. Explore the Official Documentation
The official Drupal documentation is a valuable resource for learning about attribute-based plugins:
Visit this Drupal documentation page on attribute-based plugins.
This page provides a comprehensive guide that explains:
- How to define plugins using attributes
- Available attributes for different types of plugins (blocks, fields, etc.)
- Additional considerations for using attributes in Drupal.
2. Delve into Practical Examples
While the official documentation offers a thorough explanation, practical examples can solidify your understanding. Consider these resources:
Drupalize.me Blog: This blog dives into attribute usage with specific examples, making the concepts more tangible.
Let’s Wrap It Up!
Drupal development has advanced significantly with the introduction of PHP characteristics. Features like simplicity, readability, and native integration enable developers to remain ahead of the curve and write cleaner, more maintainable code. Drupal’s continued use of this potent feature creates opportunities for a more effective and future-proof development process.
Are you prepared to use PHP attributes in Drupal projects? Leading Drupal development firm LN Webworks is here to assist you with it. Reach out to us right now to see how our proficiency with Drupal can elevate your project to new heights.
